While often neglected, ATV batteries require periodic recharging to maintain their performance and life expectancy. But how long should you charge it to get a full charge, and what can happen if you charge it too long?
The typical ATV battery charge time is about 5-10 hours, but the exact duration depends on the battery’s state of charge, battery size, charging current, battery type, and outside temperature.
This post looks at the factors that can affect charging time, recommended charging times for different battery types and sizes, and how you can estimate the charge time for your battery.
Factors That Affect ATV Battery Charge Time
Unfortunately, there is no hard and fast answer to the optimal charge time for all ATV batteries. Some batteries only need a couple of hours on the charger to reach a full charge, while others may need a full day or more.
As you will learn in this post, the answer depends on various factors, as discussed below.
Battery Size, Capacity, and Condition
ATV batteries are typically sized by a capacity rating measured in amp-hours (Ah) and Cold Cranking Amps (CCA).
Regarding battery charge time, the critical factor is the Ah rating, which indicates how much electric charge the battery can deliver without dropping below the battery’s rated voltage.
More precisely, the Ah rating is calculated by how many amps (A) the battery can deliver continuously over a specified period, typically 10 or 20 hours, multiplied by that period.
For example, a 20Ah(20H) battery can continuously deliver 20Ah/20H= 1Ah for 20 hours before the voltage drops too low.
Since Ah varies by temperature, the test is always performed at 68ºF (20ºC) for comparable results.
A battery with a rated capacity of 20Ah must be charged twice as long as a 10Ah battery to go from empty to fully charged, given we’re using the same charging current.
Check this post to learn more about ATV battery sizing (physical dimensions and capacity).
Another consideration is how the remaining battery capacity decreases with age, use, and misuse.
Charger Output and Charging Rate
When charging a battery, one of the essential charge parameters besides battery voltage (V) is the battery charge rate, which is determined by the charger output in Amps (A).
Many modern and some older chargers offer an adjustable charge output, which should be configured to match the battery’s size and capacity. Smart chargers often handle this adjustment automatically, while others require manual configuration.
The charge rate determines how fast the battery is charged.
For example, a 20Ah capacity battery must be charged twice as long at 1A than 2A to reach a full charge.
However, this doesn’t mean you can increase the charge output indefinitely to speed up the charge time.
A battery can manage only so many Amps before it no longer positively affects the charge time. Using a charge output that is too high can cause overcharging, which we’ll look into later in this post.
Some battery types, like Li-Ion, can handle a higher charge rate due to their design and can be charged faster than the other common types.
The Batteries State of Charge (SOC)
A battery state of charge (SOC) is a measurement ranging from 0% to 100% determined by the current battery voltage compared to the voltage when the battery is fully charged.
There are four main types of ATV batteries, categorized by their basic battery chemistry and design.
Because the nominal voltage varies slightly between battery types, they aren’t always at the same state of charge, even if the voltage reads the same.
For example, a Li-Ion battery at 12.9V is only at about 25% SOC, while a GEL-cell battery at the same voltage is considered fully charged, or 100% SOC.
Temperature and Environment
The temperature at which you charge the battery significantly impacts the charging process.
Lower temperatures generally slow the charging process, while warmer temperatures speed it up.
When a battery is charged, it causes a chemical process inside the battery. Charging a battery at lower temperatures slows down this chemical process, effectively reducing the battery’s ability to accept a charge.
When the temperature becomes too low, the chemical process stops altogether, and the battery won’t take a charge.
Another issue with charging a battery at sub-zero temperatures is potentially damaging the battery internals from the expanding and contracting electrolyte.
Charging a battery at higher temperatures speeds up the chemical process and increases the battery’s ability to accept a charge.
However, charging a battery at too high a temperature can cause overheating, reducing battery performance and negatively affecting the battery’s service life.
In some cases, excessive heat while charging can cause the battery to explode or leak battery acid.
That is why you should always charge the battery within the temperature range recommended by the manufacturer, typically 50 to 80 ºF (10 to 27ºC). Never attempt to charge a frozen battery.
If the outside temperature is too warm, you should avoid direct sunlight and ensure proper airflow to keep the b battery cool. In colder climates, bringing the battery inside a heated garage to charge it is a good idea. Allow some time for the battery to acclimate before connecting the charger.
Related: 3 Common Reasons Why Your ATV Battery Is Getting Hot
ATV Battery Charging Basics
You should know these battery charging basics to charge a battery safely and effectively.
Use the correct Type of Battery Charger

There are two primary types of ATV battery chargers: manual and automatic, often referred to as smart chargers. Both types are suitable for charging ATV batteries, provided they have modes with a low enough charge output for small-capacity ATV batteries.
In addition, you need to ensure you get a charger with the proper charge mode for your battery type. AGM batteries require a slightly different charge profile to charge optimally, while Li-Ion requires a Li-Ion-approved charger.
There are many benefits to choosing a smart charger over a manual charger.
- With a manual charger, you need to monitor the charging process carefully so as not to overcharge the battery.
- If something goes wrong during the charging process, most manual chargers don’t offer safety features that turn them off automatically other than a fuse.
- Smart chargers continuously monitor and adapt the charge current or voltage for an optimal charge process.
- When the battery is full, the smart charger terminates the charging process automatically and switches to a maintenance charge.
- A smart charger with maintenance mode can be left connected to keep the battery healthy while the ATV sits for long periods.
- Using a smart charger lets you leave the battery overnight and not worry about the charge time.
Prevent Overcharging
A battery can become overcharged from charging at too high of a charge current or continued charging when the battery has reached a full charge.
As a rule of thumb, the charge output should not exceed 1/10th of the battery’s rated capacity.
For example, a 20Ah battery should be charged at a rate of about 2Amps for an optimal charge without running a risk of overcharging.
Quick Charging vs. Trickle Charging
If you’re new to charging batteries, you might ask: What’s the difference between a quick charge and a trickle charge?
Quick charging is when you charge the battery at the recommended charge rate to bring it from a discharged state to a full state of charge.
Trickle charging, also known as maintenance charging, is when the charger provides a low, steady charge rate, just enough to maintain the battery’s charge level over extended periods.
Charging Safety Precautions
For your safety, whenever you’re charging a battery using an external battery charger, you must follow the safety precautions as recommended by the manufacturer, such as:
- Always wear safety goggles and gloves when working near a battery.
- Charge the battery in a well-ventilated area to vent any explosive gasses from the charging process.
- Be careful not to cause shorts as this may damage the battery or the ATV electrics and potentially cause an explosion.
I recommend checking out this post if you want a complete guide on charging any ATV battery.
How Long to Charge an ATV Battery?
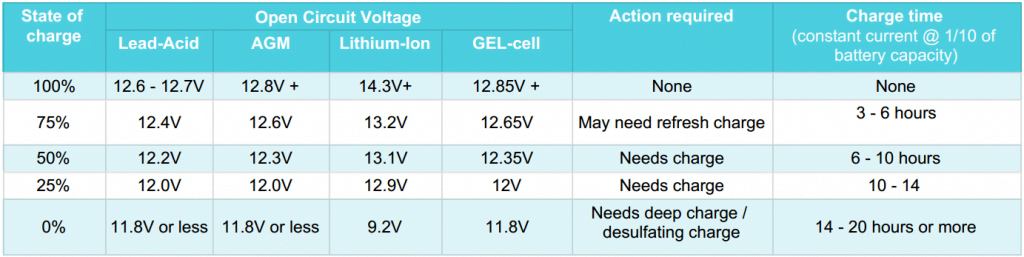
To estimate how long you should charge your ATV battery, you need to know the battery type and read its voltage to determine its state of charge.
Check this post to learn about the different battery types and this guide to learn how to read the battery voltage using a multimeter.
Refer to the table below to estimate the expected charging duration under normal charging conditions using the recommended charge rate.
How to Calculate the Charge Time
To calculate the time it takes to charge a battery, you must know its rated capacity (Ah), the charger’s output (A), and the battery type.
For example, You have a 20Ah battery at a 50% state of charge (SOC) and a 2A charger.
You might initially think it would take 20 * 50% / 2 = 5 hours to charge this battery, but that’s not entirely accurate.
You also need to consider losses, mainly due to heat generated during the charging process.
- For conventional lead-acid batteries, AGM, and GEL batteries, there’s typically a loss of around 30-40% during charging.
- Li-Ion batteries are more efficient, with only a 5-10% loss.
To estimate the approximate charge time, use this formula:
(Battery capacity * SOC) / (Charge rate * 0.6)
Using our example, it would be: 20Ah * 50% / (2A * 0.6) = 8.3 hours of charge time.
Please note that these calculations do not account for charge temperature and battery condition.
How Do I Know When My ATV Battery Is Fully Charged?
If you’re using an automatic smart charger, it will terminate the charging process and switch to a maintenance charge as soon as the battery is fully charged. Most chargers have indicator lights or displays indicating when the battery is full.
On the other hand, a manual charger does not turn off automatically and needs to be monitored closely to avoid overcharging.
Most manual chargers have an amp meter indicating the current charge rate. When the meter begins to drop to zero, you know the battery is reaching a full charge.
Related Questions
Can I Use a Car Battery Charger to Charge My ATV Battery?
It is possible to use a car battery charger to charge an ATV battery as long as it has a low-amp setting, typically around 2Aamp charge output. Charging an ATV battery at the same rate you charge a car battery, typically 8 to 10A, can cause it to overheat, which can be dangerous or harmful to the ATV and battery.
How Often Should I Charge My ATV Battery?
The average ATV owner should charge the battery to a full charge using an external battery charger once every 1 to 2 months.
If you use high-current accessories, such as when plowing snow, and drain the battery without sufficient riding time for the built-in charge system to replenish it, you may need to use an external charger more frequently.

